
So there is a technique here, you can call it u-substitution. But that's not what we have here, we have cosine of pi x. With respect to x of sine of x is equal to cosine of x. What is this equal to? Now, if we were just trying to find the antiderivative of cosine of x, it's pretty straightforward. And now let's evaluate the integral from zero to one of cosine pi, I don't need that first parentheses, of cosine of pi x dx. So this first part right over here is positive 1/2. So this is going to beĮqual to positive 1/2. Zero minus negative 1/2 is going to be equal to positive 1/2. 1/2 plus negative one, or 1/2 minus one, is negative 1/2.

If I evaluate it at zero, it's going to be zero squared over two, which is, well, I'll just write it. If I evaluate it at zero, let me do this in another color. And I'm gonna evaluate that at zero and subtract from that, it evaluated at one. It'll be x to the first, x to the first over one, which is just x. And then plus x, and you could view it as I'm just incrementing the exponent and then dividing by that value. Integral from negative one to zero of x plus one dx. And so now we just have toĮvaluate each of these separately and add them together. And then when you go from zero to one, f of x is cosine pi x. So if you look at the intervalįrom negative one to zero, f of x is x plus one. Me to split it up this way, in particular to split the integral from negative one to one, split it into two intervalsįrom negative one to zero, and zero to one? Well, I did that because x equals zero is where we switch, where f of x switchesįrom being x plus one to cosine pi x. To the definite integral from negative one to zero of f of x dx plus the integral from zero to one of f of x dx. And the way that we can make this a little bit more straightforward is to actually split up And if you were thinking that, you're thinking in the right direction.
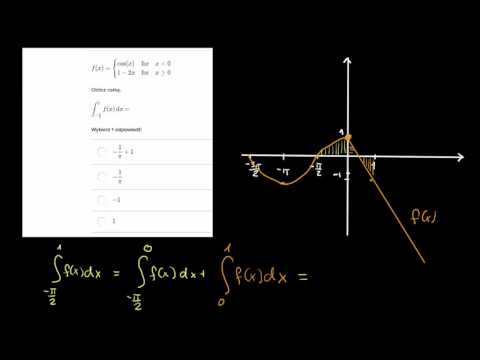
And you might immediately say, well, which of these versions of f of x am I going to take theĪntiderivative from, because from negative one to zero, I would think about x plus one, but then from zero to one I would think about cosine pi x. The definite integral from negative one to one of f of x dx. A f of x right over here and it's defined piecewiseįor x less than zero, f of x is x plus one, for x is greater than or equal to zero, f of x is cosine of pi x.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
